Paper chromatography

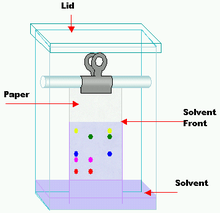
Paper chromatography is an analytical method used to separate colored chemicals or substances. It is primarily used as a teaching tool, having been replaced by other chromatography methods, such as thin-layer chromatography. A paper chromatography variant, two-dimensional chromatography involves using two solvents and rotating the paper 90° in between. This is useful for separating complex mixtures of compounds having similar polarity, for example, amino acids. The setup has three components. The mobile phase is a solution that travels up the stationary phase, due to capillary action. The mobile phase is generally mixture of non-polar organic solvent, while the stationary phase is polar organic solvent in water. Paper is used to support stationary phase (polar organic solvent). Difference between TLC and paper chromatography is that stationary phase in TLC is a layer of adsorbent (usually silica gel, or aluminium oxide), and stationary phase in paper chromatography is water. Paper chromatography is an analytical method used to separate colored chemicals or substances. It is primarily used as a teaching tool, having been replaced by other chromatography methods, such as thin-layer chromatography. A paper chromatography variant, two-dimensional chromatography involves using two solvents and rotating the paper 90° in between. This is useful for separating complex mixtures of compounds having similar polarity, for example, amino acids. The setup has three components. The mobile phase is a solution that travels up the stationary phase, due to capillary action. The mobile phase is generally mixture of non-polar organic solvent, while the stationary phase is polar organic solvent in water. Paper is used to support stationary phase (polar organic solvent). Difference between TLC and paper chromatography is that stationary phase in TLC is a layer of adsorbent (usually silica gel, or aluminium oxide), and stationary phase in paper chromatography is water. The retention factor (Rƒ) may be defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the solute to the distance traveled by the solvent. It is used in chromatography to quantify the amount of retardation of a sample in a stationary phase relative to a mobile phase. Rƒ values are usually expressed as a fraction of two decimal places. For example, if a compound travels 9.9 cm and the solvent front travels 12.7 cm, the Rƒ value = (9.9/12.7) = 0.779 or 0.78. Rƒ value depends on temperature and the solvent used in experiment, so several solvents offer several Rƒ values for the same mixture of compound. A solvent in chromatography is the liquid the paper is placed in, and the solute is the ink which is being separated. Paper chromatography is one method for testing the purity of compounds and identifying substances. Paper chromatography is a useful technique because it is relatively quick and requires only small quantities of material. Separations in paper chromatography involve the same principles as those in thin layer chromatography, as it is a type of thin layer chromatography. In paper chromatography, substances are distributed between a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The stationary phase is the water trapped between the cellulose fibers of the paper. The mobile phase is a developing solution that travels up the stationary phase, carrying the samples with it. Components of the sample will separate readily according to how strongly they adsorb onto the stationary phase versus how readily they dissolve in the mobile phase. When a colored chemical sample is placed on a filter paper, the colors separate from the sample by placing one end of the paper in a solvent. The solvent diffuses up the paper, dissolving the various molecules in the sample according to the polarities of the molecules and the solvent. If the sample contains more than one color, that means it must have more than one kind of molecule. Because of the different chemical structures of each kind of molecule, the chances are very high that each molecule will have at least a slightly different polarity, giving each molecule a different solubility in the solvent. The unequal solubility causes the various color molecules to leave solution at different places as the solvent continues to move up the paper. The more soluble a molecule is, the higher it will migrate up the paper. If a chemical is very non-polar it will not dissolve at all in a very polar solvent. This is the same for a very polar chemical and a very non-polar solvent.