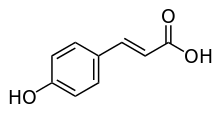
p-Coumaric acid

p-Coumaric acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, an organic compound that is a hydroxy derivative of cinnamic acid. There are three isomers of coumaric acid—o-coumaric acid, m-coumaric acid, and p-coumaric acid—that differ by the position of the hydroxy substitution of the phenyl group. p-Coumaric acid is the most abundant isomer of the three in nature. p-Coumaric acid exists in two forms trans-p-coumaric acid and cis-p-coumaric acid. p-Coumaric acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, an organic compound that is a hydroxy derivative of cinnamic acid. There are three isomers of coumaric acid—o-coumaric acid, m-coumaric acid, and p-coumaric acid—that differ by the position of the hydroxy substitution of the phenyl group. p-Coumaric acid is the most abundant isomer of the three in nature. p-Coumaric acid exists in two forms trans-p-coumaric acid and cis-p-coumaric acid. It is a crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water, but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. p-Coumaric acid can be found in Gnetum cleistostachyum. p-Coumaric acid can be found in a wide variety of edible plants such as peanuts, navy beans, tomatoes, carrots, basil and garlic. It is found in wine and vinegar. It is also found in barley grain. p-Coumaric acid from pollen is a constituent of honey. p-Coumaric acid glucoside can also be found in commercial breads containing flaxseed. Diesters of p-coumaric acid can be found in carnauba wax. It is biosynthesized from cinnamic acid by the action of the P450-dependent enzyme 4-cinnamic acid hydroxylase (C4H). It is also produced from L-tyrosine by the action of tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL).