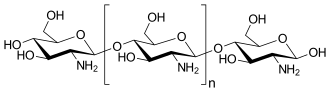
Chitosan

Chitosan /ˈkaɪtəsæn/ is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine (deacetylated unit) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated unit). It is made by treating the chitin shells of shrimp and other crustaceans with an alkaline substance, like sodium hydroxide. Chitosan has a number of commercial and possible biomedical uses. It can be used in agriculture as a seed treatment and biopesticide, helping plants to fight off fungal infections. In winemaking, it can be used as a fining agent, also helping to prevent spoilage. In industry, it can be used in a self-healing polyurethane paint coating. In medicine, it is useful in bandages to reduce bleeding and as an antibacterial agent; it can also be used to help deliver drugs through the skin.